Understanding the biomechanics of sport and exercise can improve performance and prevent injuries. It’s a fascinating field that combines biology and physics to analyze movement.
Athletes and trainers use biomechanics to optimize technique. By studying how muscles, bones, and joints work together, we can enhance efficiency in sports activities. This knowledge is crucial for both professional athletes and fitness enthusiasts. It helps them achieve their goals while minimizing the risk of injury.
Exploring biomechanics can lead to better training methods and improved athletic performance. In this blog, we’ll dive into the basics of biomechanics, its importance in sports, and how it can benefit you. Whether you’re a coach, athlete, or just curious, this guide will provide valuable insights into the mechanics of human movement.
Introduction To Biomechanics
Understanding the biomechanics of sport and exercise can greatly enhance performance and reduce injury risks. This field blends mechanics with the human body to analyze movements. Let’s dive into the basics of biomechanics.
Importance In Sport
Biomechanics holds significant importance in sports for various reasons:
- Performance Enhancement: Analyzing movements can help athletes improve their techniques.
- Injury Prevention: Understanding body mechanics aids in identifying risky movements.
- Rehabilitation: It assists in designing effective recovery programs.
In essence, biomechanics bridges the gap between science and sports performance.
Core Concepts
There are several core concepts within biomechanics that are crucial to understand:
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Kinematics | Study of motion without considering its causes. |
| Kinetics | Examines forces causing motion. |
| Dynamics | Focuses on forces and their effects on motion. |
| Statistical Mechanics | Analyzes systems in equilibrium. |
Understanding these concepts can help in breaking down complex movements into simpler components.

Credit: www.amazon.com
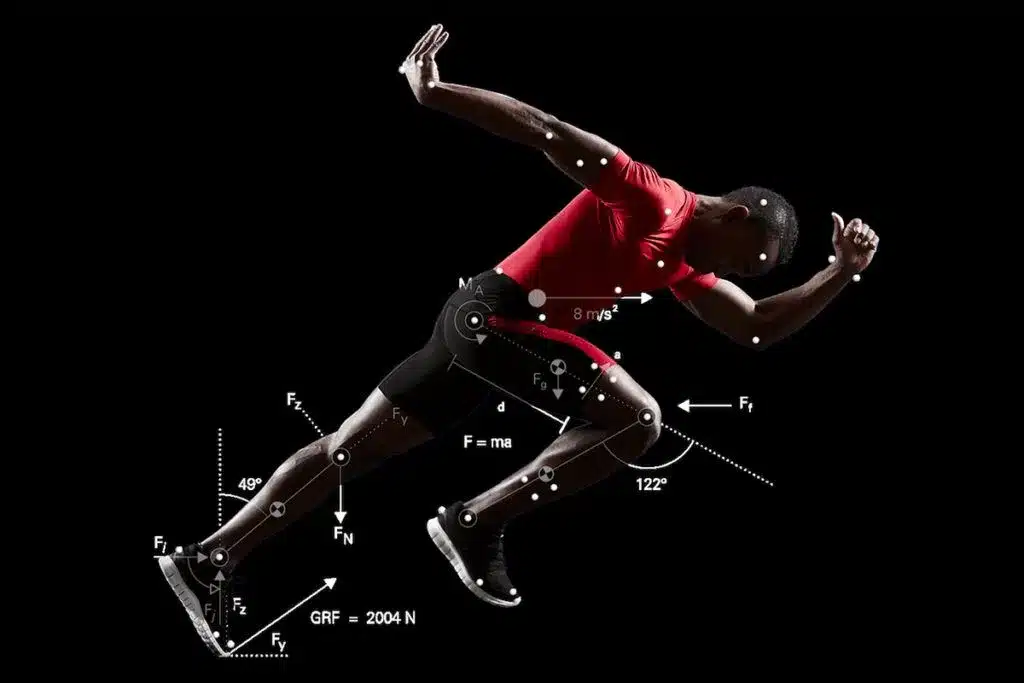
Movement Analysis
Movement analysis in biomechanics is crucial for understanding sports and exercise. It helps in evaluating and improving performance. This section focuses on two main components: kinematics and kinetics.
Kinematics
Kinematics deals with the motion of objects without considering the forces causing the motion. It looks at aspects like speed, velocity, and acceleration. In sports, kinematics helps in analyzing the movement patterns of athletes. By studying these patterns, coaches can optimize training methods.
Kinematic analysis often uses video recordings. These recordings capture the athlete’s movements in real-time. Software tools then break down these recordings into measurable data. This data includes joint angles, stride lengths, and body positions. Such detailed analysis helps in identifying areas for improvement.
Kinetics
Kinetics, on the other hand, focuses on the forces causing motion. It examines how muscles, gravity, and other forces interact during movement. Understanding these forces is essential for preventing injuries. It also helps in enhancing performance by optimizing force application.
Force plates are commonly used in kinetic analysis. These devices measure the ground reaction forces generated by the athlete. The data obtained from force plates can indicate how much force is applied during activities like jumping or sprinting. This information aids in adjusting training regimens to improve efficiency and safety.
Both kinematics and kinetics play vital roles in movement analysis. Together, they provide a comprehensive view of an athlete’s performance. This holistic approach helps in fine-tuning techniques and achieving better results.
Muscle Function
Understanding muscle function is key to improving sports performance. Muscles are responsible for movement. They contract and produce force. This aids athletes in various physical activities. Let’s delve deeper into muscle contraction and force production.
Muscle Contraction
Muscle contraction is a complex process. It starts in the brain. The brain sends signals to the muscles. These signals trigger contractions. There are two main types of muscle contractions. These are isotonic and isometric contractions.
Isotonic contractions involve movement. The muscle changes length. Examples include lifting weights or running. Isometric contractions do not involve movement. The muscle length stays the same. An example is holding a plank position.
Force Production
Force production is essential in sports. It determines how well an athlete can perform. Muscles produce force through contraction. The amount of force depends on several factors. These include muscle size, type, and the speed of contraction.
Larger muscles can produce more force. Muscle fibers also play a role. There are two main types of muscle fibers. Fast-twitch fibers are for short bursts of power. Slow-twitch fibers are for endurance activities. Training can enhance force production. Strength training, in particular, is effective.
Understanding these aspects helps athletes improve. They can tailor their training to their needs. This leads to better performance in their sport.
Joint Mechanics
Understanding joint mechanics is crucial for athletes and fitness enthusiasts. Joints are the body’s hinges, allowing movement and flexibility. Proper joint function is vital for optimal performance and injury prevention. Let’s dive deeper into joint structure and movement patterns.
Joint Structure
Joints connect bones and enable movement. They consist of cartilage, synovial fluid, and ligaments. Cartilage cushions the bones, reducing friction. Synovial fluid lubricates the joints, ensuring smooth motion. Ligaments provide stability, preventing excessive movement.
Movement Patterns
Joints facilitate various movement patterns. These include flexion, extension, rotation, and abduction. Flexion decreases the angle between two bones. Extension increases it. Rotation involves moving a bone around its axis. Abduction moves a limb away from the body’s midline.
Understanding these patterns helps in designing effective training programs. It ensures that exercises target the correct muscles and joints. This knowledge also aids in preventing injuries. Proper alignment and movement reduce strain on joints. This enhances performance and prolongs athletic careers.
Injury Prevention
Injury prevention in sports and exercise is crucial. Athletes often push their limits. This makes them more prone to injuries. Understanding biomechanics can help prevent these injuries. It ensures athletes train safely and effectively. Let’s dive into common injuries and preventative techniques.
Common Injuries
Many athletes face injuries. Sprains and strains are very common. These happen when muscles or ligaments stretch too far. Knee injuries, like ACL tears, are also frequent. Overuse injuries such as tendonitis can occur. Stress fractures from repetitive motion often affect runners. Understanding these injuries can help in preventing them.
Preventative Techniques
Proper warm-up and cool-down routines are essential. Warm muscles are less likely to get injured. Regular strength training helps too. Strong muscles support joints better. Using the right equipment is crucial. Good shoes can prevent foot and leg injuries. Proper techniques in sports are vital. Incorrect form can lead to serious injuries. Rest and recovery are important. Overworking the body can cause harm. Listen to your body. If something feels wrong, take a break.
Performance Enhancement
Performance Enhancement in sports and exercise is a multifaceted concept. It involves optimizing physical capabilities through science-based approaches. This section delves into two critical aspects: Training Methods and Technological Advances.
Training Methods
Effective training methods are the backbone of performance enhancement. Athletes use these methods to improve their strength, speed, and endurance.
Strength training involves exercises that increase muscle power. Common techniques include:
- Weight lifting
- Resistance bands
- Bodyweight exercises
Speed training focuses on improving quickness and agility. Popular methods are:
- Sprint drills
- Plyometrics
- Agility ladders
Endurance training aims to enhance stamina. It includes:
- Long-distance running
- Cycling
- Swimming
Technological Advances
Technological advances play a significant role in performance enhancement. Modern technologies help athletes train more effectively and safely.
Wearable devices, such as fitness trackers, monitor vital signs. This data helps in:
- Adjusting training intensity
- Preventing overtraining
- Tracking progress
Biomechanical analysis uses cameras and sensors. This technology provides insights into movement patterns. Benefits include:
- Identifying inefficiencies
- Improving technique
- Reducing injury risk
Virtual reality (VR) is also emerging. It simulates real-world scenarios for:
- Enhanced mental preparation
- Safe practice environments
- Skill refinement
Biomechanical Assessments
Biomechanical assessments play a vital role in sports and exercise. They help understand how the body moves. This knowledge aids in improving performance and preventing injuries. Two key tools used in these assessments are motion capture and force plates.
Motion Capture
Motion capture tracks body movements with high precision. It uses cameras and sensors. These devices record the position of markers placed on the body. The data provides detailed information about joint angles and limb velocities. Athletes can then correct their techniques. This method is widely used in various sports, including running and swimming.
Force Plates
Force plates measure the forces exerted by the body on the ground. They help assess balance and movement efficiency. Athletes stand, jump, or run on these plates. The plates capture data on forces applied during these actions. This information helps in designing better training programs. Coaches use it to adjust an athlete’s technique to reduce injury risk.
Credit: store.cedarville.edu
Case Studies
The biomechanics of sport and exercise is a fascinating field. It helps us understand how our bodies move. Through various case studies, we can see real-world applications. These studies highlight how biomechanics can improve athletic performance. They also show how it can prevent injuries.
Athlete Success Stories
Many athletes have benefited from biomechanics. For example, a sprinter improved his running technique. He reduced his race time by 0.5 seconds. Another case involved a basketball player. She learned to jump higher. This helped her score more points.
A cyclist also saw great results. He adjusted his posture and pedaling style. His endurance and speed improved significantly. These success stories show the power of biomechanics. Simple changes can make a big difference.
Lessons Learned
Each case study teaches us valuable lessons. From the sprinter, we learned the importance of technique. Small changes can lead to big improvements. The basketball player’s story highlights the role of biomechanics in enhancing skills. Jumping higher gave her a competitive edge.
The cyclist’s experience shows how posture affects performance. Proper alignment reduces strain and boosts efficiency. These lessons are crucial for athletes. They help them reach their full potential. Understanding biomechanics can lead to smarter training and better results.
Future Of Biomechanics
The future of biomechanics in sport and exercise holds much potential. This field will shape how athletes train, perform, and recover. Recent advancements are paving the way for new discoveries.
Emerging Trends
Wearable technology is a major trend. Smart devices now track movement, muscle activity, and more. These gadgets provide real-time data to athletes and coaches. They help in making informed decisions. Improved materials and design in sports equipment are also emerging. These innovations enhance performance and reduce injury risks.
Research Directions
Research in biomechanics is expanding. Scientists are exploring muscle-tendon dynamics in greater detail. This knowledge helps in understanding how muscles work during exercise. Another focus is on personalized training programs. These programs consider an athlete’s unique biomechanical profile. By doing so, they optimize training effectiveness and safety.
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are new areas of interest. These technologies offer immersive training environments. Athletes can practice in varied, controlled settings. This aids in skill development and strategy planning.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Biomechanics In Sport?
Biomechanics in sport studies the movement of the human body. It applies principles of mechanics to optimize performance and prevent injuries.
How Does Biomechanics Improve Athletic Performance?
Biomechanics helps athletes improve performance by analyzing movements. It identifies inefficiencies and suggests improvements for better technique and results.
Why Is Biomechanics Important In Exercise?
Biomechanics ensures exercises are performed safely and effectively. It helps prevent injuries by promoting proper form and movement patterns.
What Tools Are Used In Biomechanics Analysis?
Common tools include motion capture systems, force plates, and wearable sensors. These tools provide detailed data on body movements and forces.
Conclusion
Understanding the biomechanics of sport and exercise is crucial. It enhances performance and reduces injury risk. Athletes gain insights into their movements. Coaches can make better training decisions. Overall, biomechanics offers valuable benefits. Everyone involved in sports should consider this field.
It brings science and sports closer together. This knowledge supports success and longevity in athletic careers. Keep exploring and applying these principles. Your body will thank you.



